Interstitial lung disease is an umbrella term used to define a complex group of pulmonary diseases, including sarcoidosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sarcoidosis is a systemic inflammatory disease with a predilection for the respiratory system. Although most patients enter remission and have good long-term outcomes, up to 20% develop fibrotic lung disease, whereby granulomatous inflammation evolves to pulmonary fibrosis. The development of pulmonary fibrosis is associated with significant morbidity and can be fatal. Dyspnea, cough, and hypoxemia are frequent clinical manifestations. Pulmonary function testing often demonstrates restriction from parenchymal involvement, although airflow obstruction from airway-centric fibrosis is also recognized.
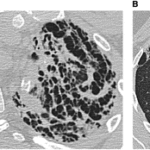
Honeycombing in fibrotic pulmonary sarcoidosis
« Back to Glossary Index
